Basiq: Building a more inclusive CDR ecosystem with a ‘Consumer Service Provider’ model
Fintechs offer valuable lessons for the CDR and Open Banking
Basiq is a CDR-accredited Open Banking platform providing fintechs with the building blocks of financial services, whether it’s access to financial data or tooling. At the heart of the CDR (Consumer Data Right) and Open Banking is the consumer-consented sharing of data to accelerate innovation, drive competition, promote transparency and increase consumer benefit.
Since 2017, Basiq has been carrying out this mission by enabling fintechs to leverage open financial data, with clients ranging from some of Australia’s largest fintechs, to startups in pre-launch stage.
The fintech experience provides valuable lessons for CDR’s rollout, from a practical, use cases focused perspective. As such, Basiq has taken the opportunity to provide feedback to Treasury on version 3 of the proposed changes to CDR rules, with the purpose of championing the voice of fintechs of all sizes.
Summary of the CDR rules amendments (version 3)
As it stands, the CDR is still in its infancy, with complex rules and a resource-intensive path to participation. Version 3 of the proposed changes to the Consumer Data Right and, in particular, tiered accreditation and sponsorship models have been hailed as a step forward in building a more inclusive Open Banking ecosystem.
Overall, the move to enable access to CDR data without the prerequisite of becoming a fully accredited data recipient (ADR) is welcomed, however, the levels of responsibility, liability and data accessibility varied greatly amongst the proposed models and added undue complexity.
As an example, the ‘Principal CDR representative model’ would absolve any third party of responsibility over the data they hold and place full liability on the ADR. On the other hand, the ‘Sponsorship model’ is unclear about what ‘shared liability’ entails and is very similar to full ADR accreditation. In contrast, the ‘Trusted Advisor model’ doesn’t take into account the need to provide persons with a base level of education around the security and governance of CDR data.
Building a more inclusive ecosystem with a ‘Consumer Service Provider’ model
To better balance the governance structure needed to support the ecosystem whilst reducing barriers to participation, Basiq proposes a simplified single ‘Consumer Service Provider’ model that works based on four principles.
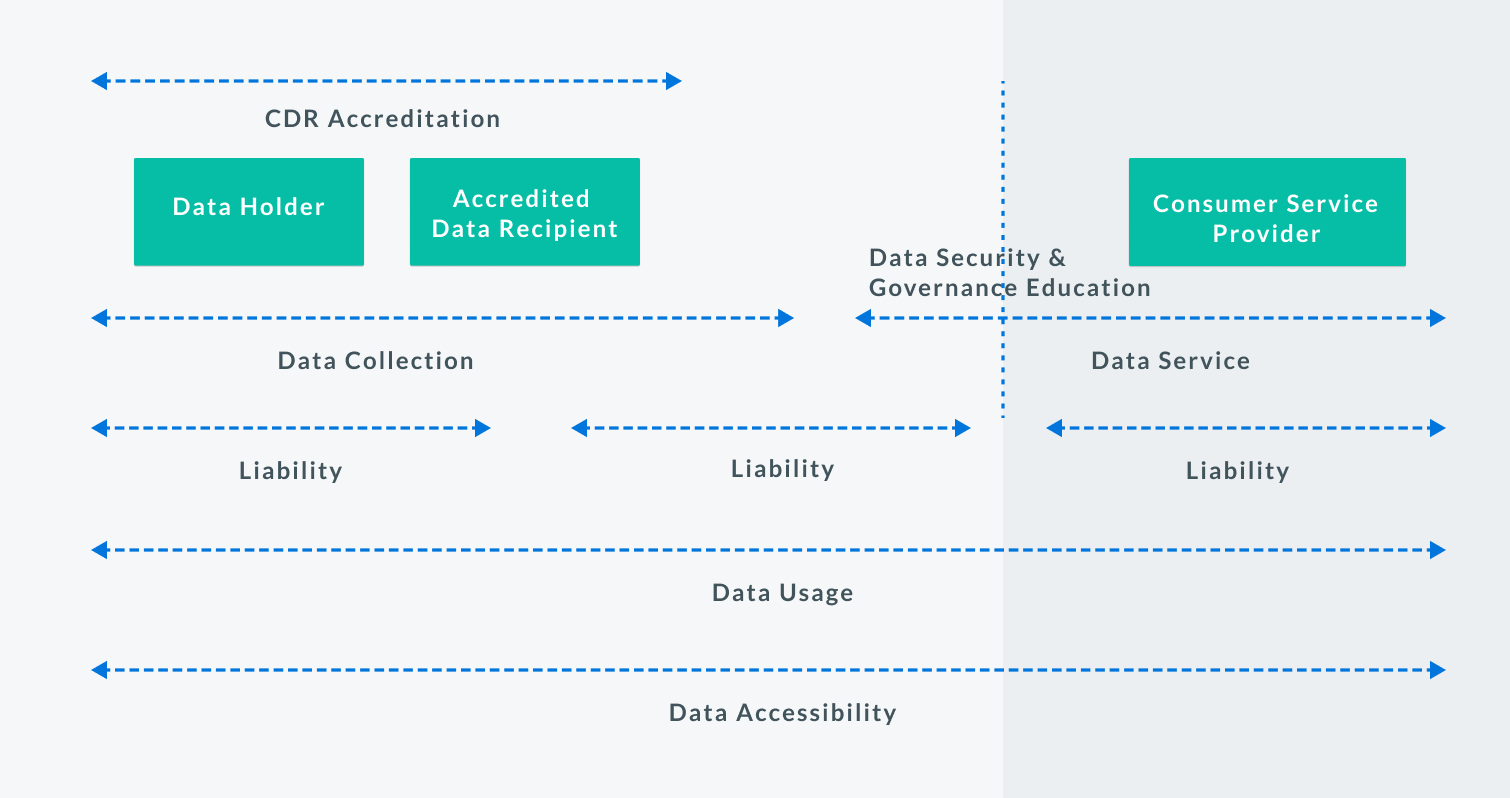
1) CDR data should be shareable with non ADRs. Many businesses already handle sensitive customer data i.e. banking, passports and medical data. If these businesses are able to seek consumer consent and handle the data in a safe and CDR-compliant manner, then non-accreditation should not prohibit them from doing so.
2) ADRs that require direct access and communication with Data Holders should continue to be regulated as per current requirements.
3) ADRs should be responsible for educating third parties on data security and governance.
4) Each party should ultimately be responsible for their own actions in the handling of CDR data.
The above principles are focused on facilitating greater participation and innovation to accelerate the delivery of more personalised, data-driven offerings benefiting consumers. For consumers, the process of consenting and sharing data is simply a stepping stone to accessing a broader range of financial products. Similarly, for fintechs, the benefit of the CDR lies in what they can build with Open Banking data, rather than how to access it.